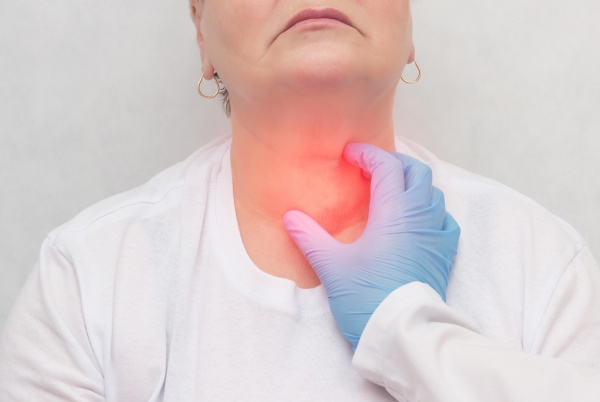
Hashimoto’s disease, also known as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis, is an autoimmune disorder in which your immune system attacks your thyroid gland, causing damage to thyroid cells. The thyroid gland is a small butterfly-shaped gland located below your Adam’s apple. As part of the endocrine system, this gland releases thyroid hormone involved in the regulation of metabolic activity.
In cases of Hashimoto’s disease, your body forms self-attacking antibodies (Confused Antibodies) that destroy portions of the thyroid gland. Signs and symptoms of Hashimoto’s disease may take years before it becomes clinically apparent, however, the inflammation caused by these antibodies continue—affecting different parts of the thyroid gland .
With the progression of Hashimoto’s disease, the thyroid gland becomes diffusely nodular, eventually becoming under-active. An underactive gland produces decreased amount of thyroid hormone, eventually causing decreased metabolic activity (hypothyroidism).